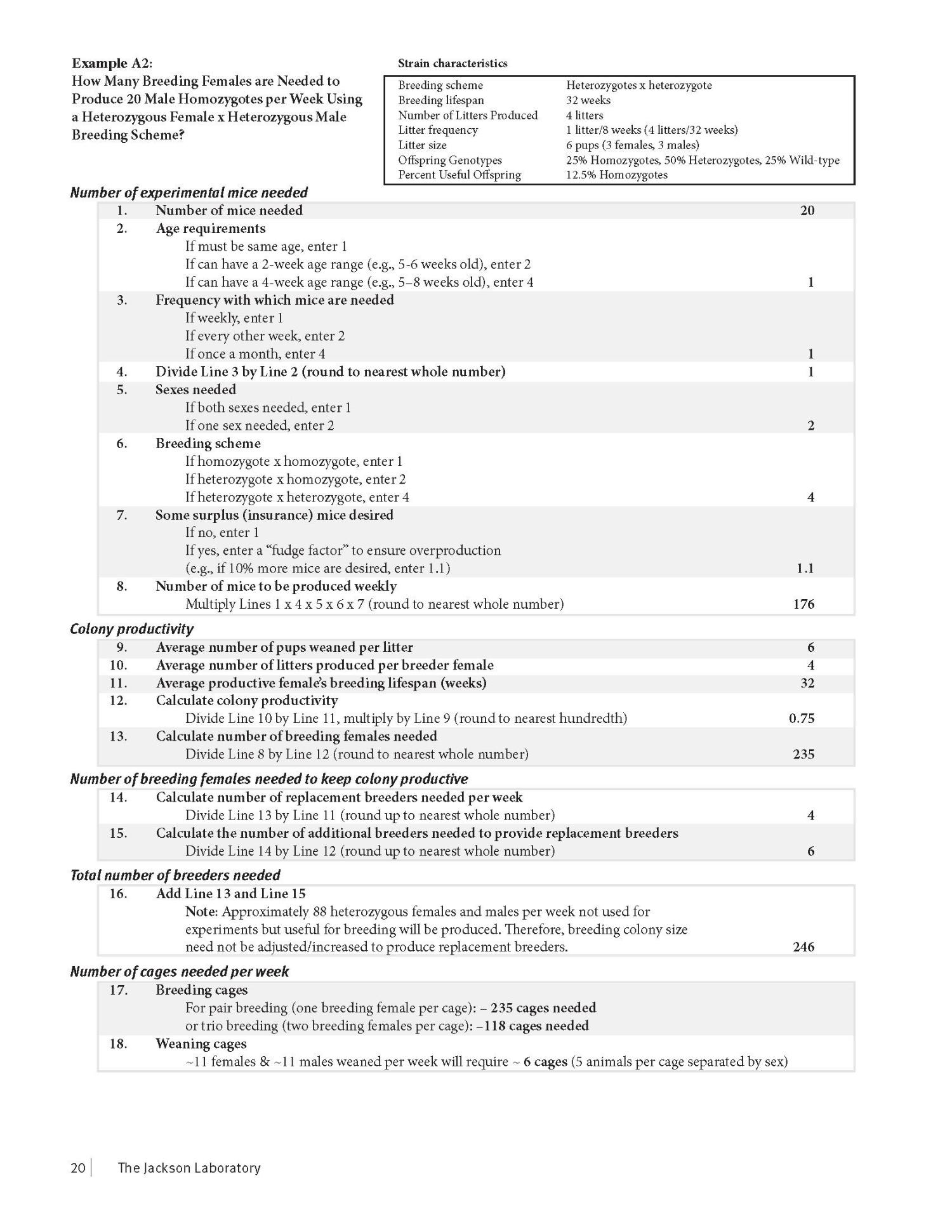
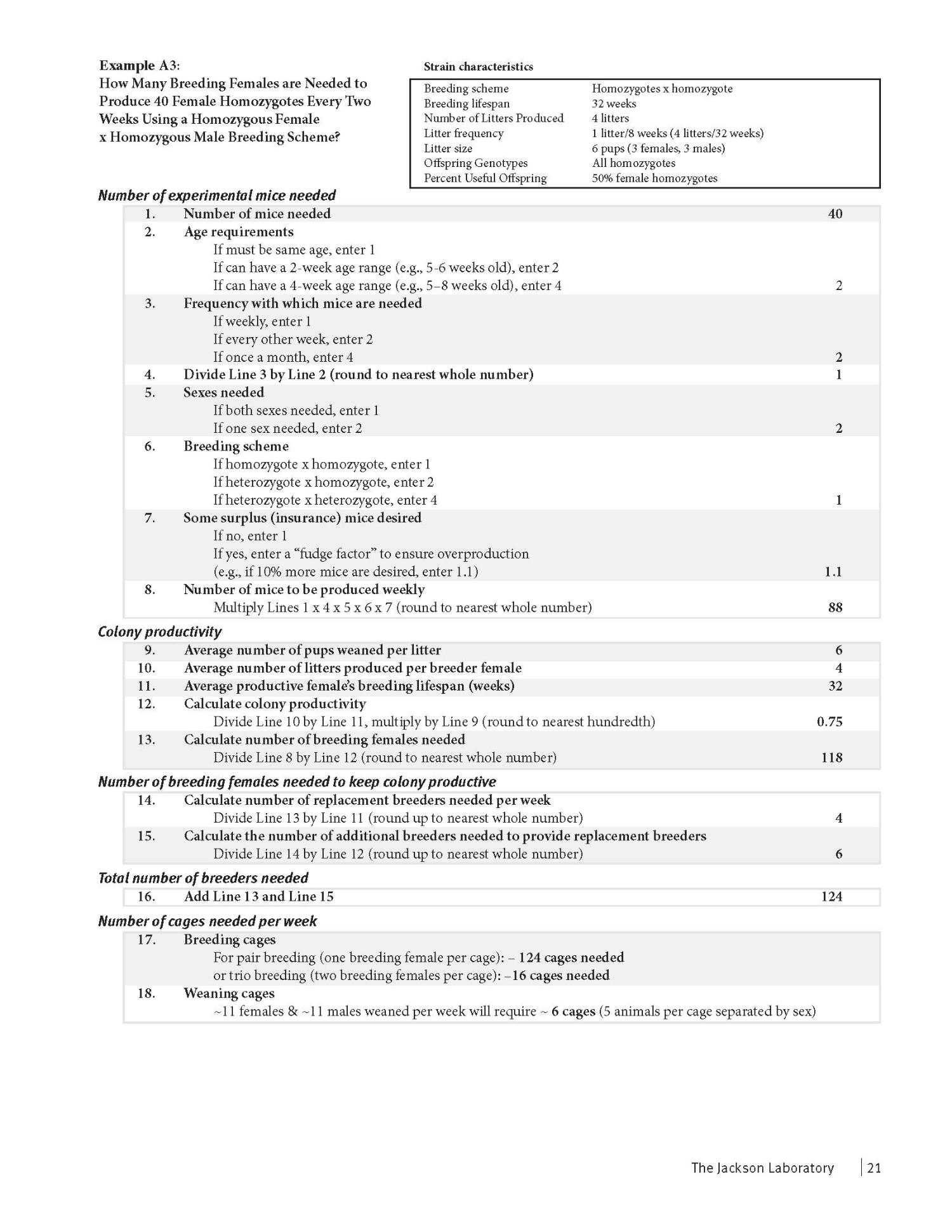
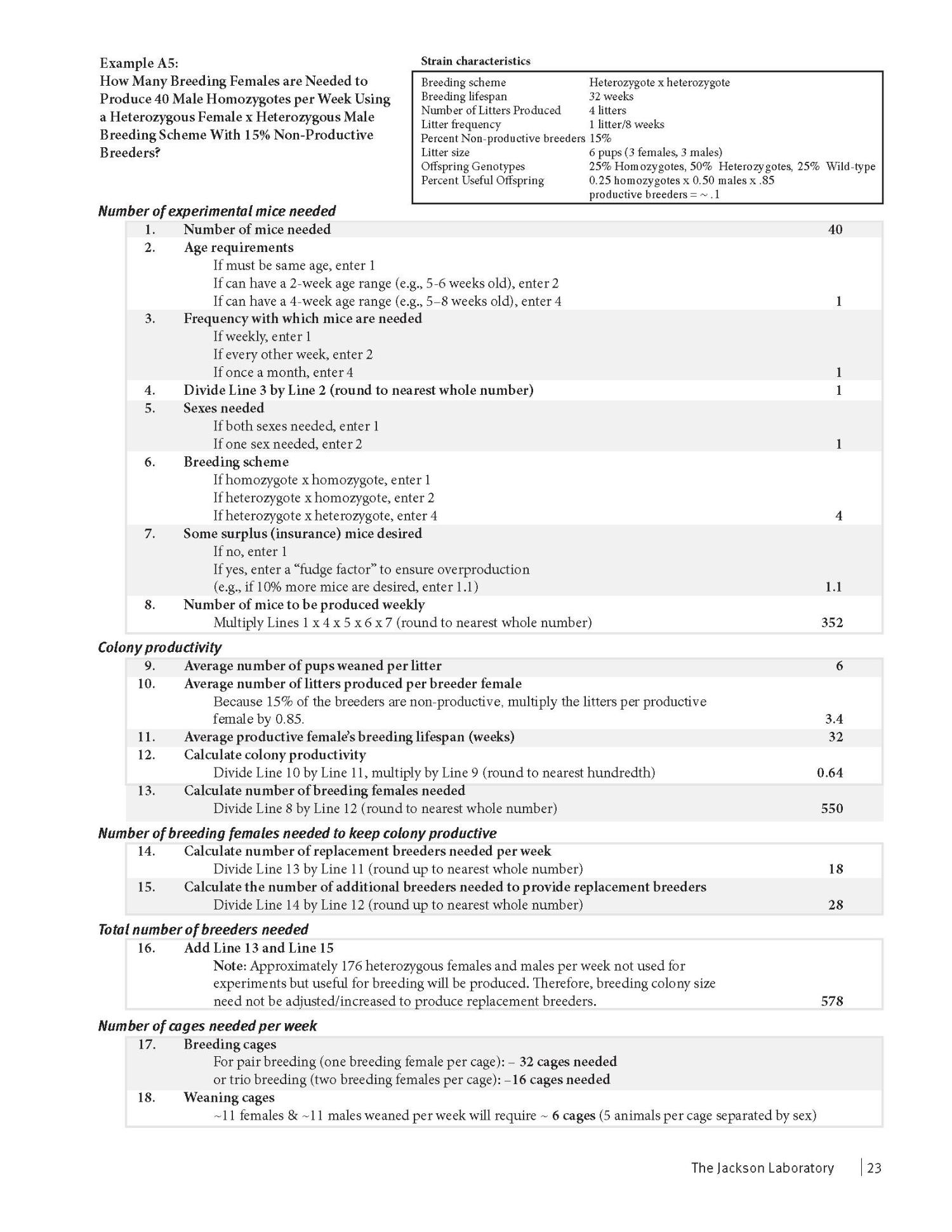
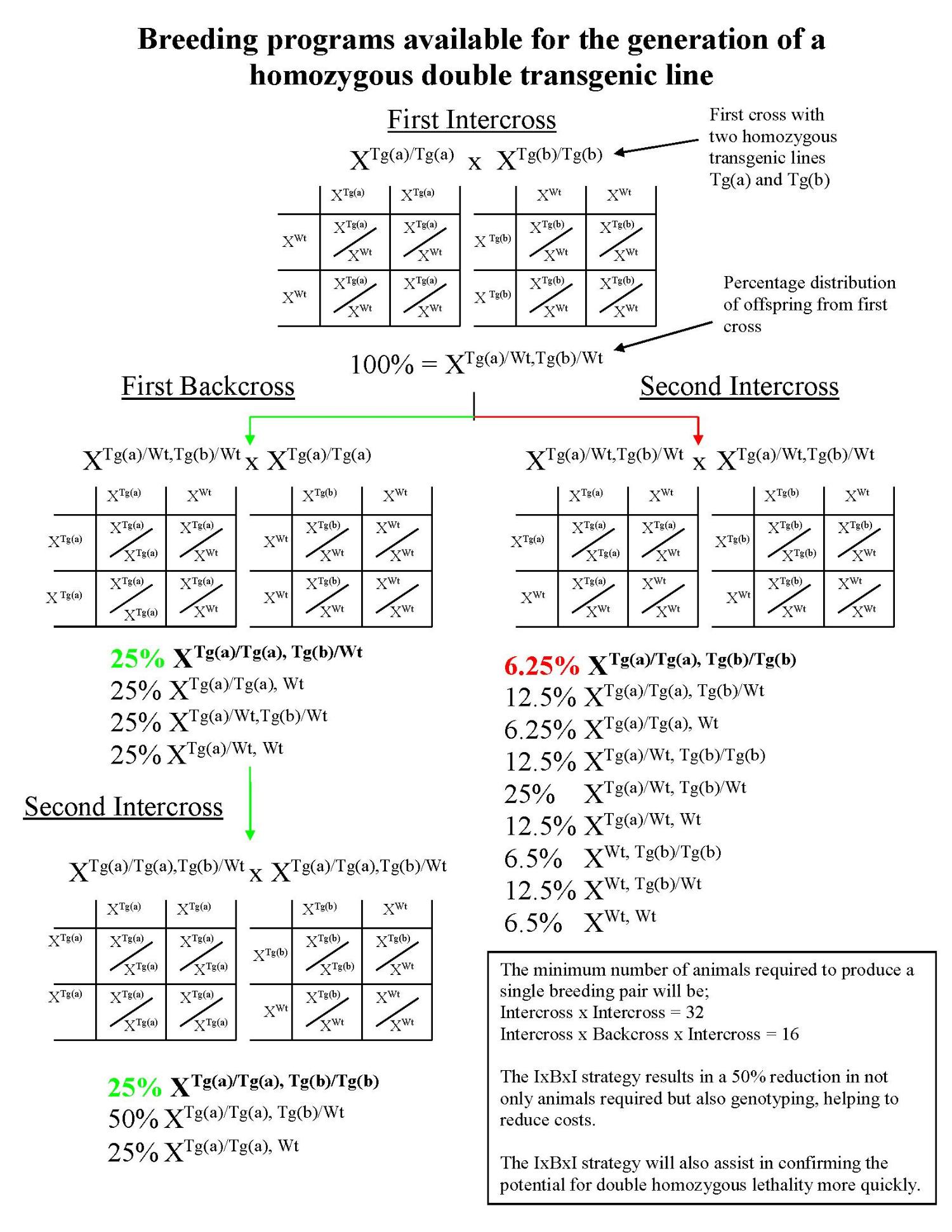
Jax guidelines for calculating breeding animal numbers required to produce research quota:
Strains Phenotype
A summary of phenotypes of commonly used mouse strains
|
Strain |
Details |
|
129X1/SvJ |
Low overall tumor incidence (7% in males and 21% in females) in mice >18 months. High incidence of urinary calculi, leading to possible bladder stones. |
|
A/J |
Low intra-strain aggression High social dominance of males in competition for females Mammary adenocarcinomas (=mammary tumours) 0% in males 1% in virgin females and 28% in breeding females 90% of mice develop pulmonary tumours (=lung tumour) by 18 months 20% of mice at 6 months develop spontaneous lung tumours Up to 10% of newborns develop congenital malformations including, cleft lip and plate and polydactyly (=additional toes) 4% of new borns have open eye lids High ratio of females at birth Sterility reported in 11.5% of mice in 1973 |
|
AKR |
High intrastrain aggression. Best known for its high incidence of Lymphatic Leukaemia, developed by 70-80% of males and 80-90% of females by 18 months. Symptoms include fever and enlargement of the lymph nodes. |
|
BALB/c |
High intrastrain aggression. High Social dominance of males in competition for females. Mammary tumours 10% in females at 14 months; 20% in females at 16 months Heart defects such as cardiac Calcinosis (=build up of calcium salts) are common in ex-breeder mice 17-62% No recorded incidence of spontaneous congenital malformations High proportion of time spent sleeping Accessory spleens found in 20% of animals The number of nipples commonly exceeds five pairs Embryos subject to in-vitro 2-cell block and grow more successfully from the late 2-cell stage on. Sterility reported in 32% of mice in 1973 |
|
C3H/HeJ |
Low intrastrain aggression Carries the retinal degeneration gene and is capable of discriminating patterns up to 40 days of age. Hepatomas (=tumour of the liver) 72-91% males at 14 months; 59% virgin females at 14 months; 30-38 % breeding females at 14 months Tail lesions similar in appearance to bit wounds have been recorded Females have a shorter and less regular oestrus cycle then C57BL/6J mice. Early opening of the vagina, but late onset of cyclicity. Sterility reported in 10% of mice in 1973 |
|
C57BL/6J |
Resistant to audiogenic seizures Very low incidence of tumours in both sexes 0-1% Develop congenital abnormalities including; Micropphthalmia (=small eyes) and anophthalmia (=absence of one or both eyes) at 8- 20%, polydactyly (=additional toes) and otocephaly (=lack of lower jaw) have also been recorded Susceptible to hydrocephalus at 1-3% Genetically predisposed to age-related hearing loss Mice have a rapid and shallow breathing pattern in contrast to C3H mice Sterility reported in 8% of mice in 1973 |
|
C57BL/10ScSn |
More suceptable to tumours then C57BL/6J, but still considered low. Develop congenital abnormalities including; Micropphthalmia (=small eyes) and anophthalmia (=absence of one or both eyes) at 8- 20%, polydactyly (=additional toes) and otocephaly (=lack of lower jaw) have also been recorded Susceptible to hydrocephalus at 1-3% |
|
CBA/CaH |
Low intrastrain aggression Short life span of males associated with high incidence of haemothorax (=collection of blood around the lungs leading to collapse of lung) High gross tumour development in older animals High proportion of time spent sleeping Sterility reported in 5.2% of mice in 1973 |
|
DBA/1 |
Low gross tumour incidence in males |
|
DBA/2 |
Low social dominance of males in competition for females Susceptible to audiogenic seizures Genetically predisposed to age-related hearing loss Sterility reported in 31% of mice in 1973 Has shorter and less regular oestrus cycles than C57BL/6J |
|
FVB/n |
Have a high tendency towards an "idiosyncratic neurobehavioral disorder" affecting 20-57% of a population, with tendencies towards females. This can result is sudden mood swings with aggression. These mice also carry the retinal degeneration gene and will suffer blindness |
|
NOD/LtJ |
About 80% of females and 20% of males develop insulin-dependent diabetes (Type I diabetes) by the age of 30 weeks, although this will vary with environmental conditions |
|
SJL/J |
High spontaneous fighting Severe fighting among males housed together, beginning at 8 weeks Reticulum cell carcinomas (= ) appear in 90% or animals at 13 months of age. High susceptibility to subretinal tumours at 9 days of age |
Information sourced from Festing’s index of inbred strains